Gangrene is a serious medical condition that develops when body tissues do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients due to poor blood circulation or severe infection. This condition may occur suddenly after an injury or develop gradually due to long-term health problems such as diabetes and vascular disease.
Clinical experience shows that early diagnosis and specialized gangrene care play a critical role in protecting healthy tissue, controlling infection, and improving recovery outcomes.
Gangrene occurs when body tissue dies because of a lack of blood supply, infection, or both. It most commonly affects the feet, toes, fingers, hands, and legs, but it can also develop internally.
Without timely medical care, gangrene can spread quickly and lead to serious and May lead to serious medical complications. Early medical attention significantly improves treatment success.
Gangrene is a medical emergency. If you notice any signs of tissue death, seek immediate medical attention to prevent serious complications.
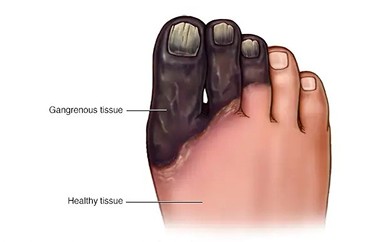
Dry gangrene develops when blood flow to a body part is slowly reduced without active infection. The affected area often becomes dry, cold, shriveled, and dark in color. This type is commonly seen in Individuals with long-term circulation issues.
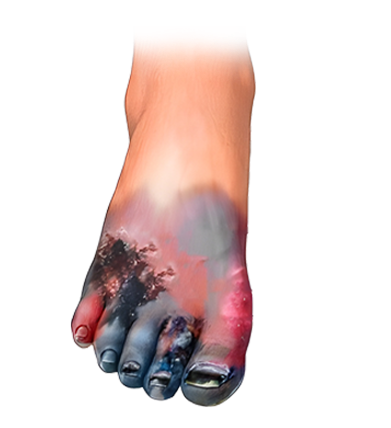
Wet gangrene occurs when dead tissue becomes infected, causing swelling, fluid buildup, and rapid tissue breakdown. Medical professionals consider this form an emergency because it spreads quickly.
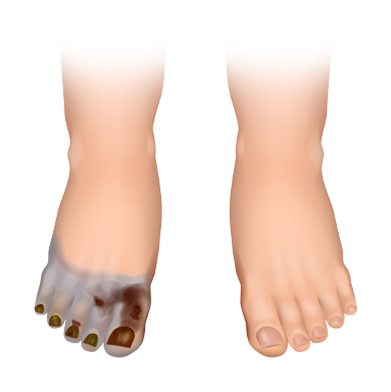
Gas gangrene is a rare but life-threatening condition caused by bacteria that produce gas and toxins inside the tissue. These toxins destroy muscle tissue rapidly and require immediate medical care.
Early symptoms of gangrene may be mild but can worsen rapidly.
pale, blue, purple, or black
Affected area feels cold and loses sensation
Sharp pain or sudden numbness
Fluid-filled blisters and tissue swelling
Unpleasant odor from affected tissue
Elevated temperature and general fatigue
If you notice any combination of these symptoms, especially skin discoloration with pain or numbness, seek emergency medical care immediately.
People at higher risk of gangrene include:
If gangrene is not treated promptly, it may result in:
Gangrene commonly affects:
Medical experts emphasize that gangrene can often be prevented by:
Proper cleaning and care of wounds
Regular foot and skin examinations
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels
Avoiding smoking
Seeking early medical care for slow-healing wounds
Schedule medical examinations
Wear protective shoes
Protect from extreme temps
Gangrene diagnosis involves:
Physical examination by experienced medical professionals
Blood tests to identify infection
Imaging tests such as X-ray, CT scan, or MRI
Wound or tissue cultures in infected cases
Gangrene treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition. Care plans are customized and may include:
Vascular procedures and medications to restore blood flow
Specialized dressings and hyperbaric oxygen treatment
Targeted antibiotic therapy and infection management
Surgical debridement to prevent infection spread
Regular assessments and long-term follow-up care
