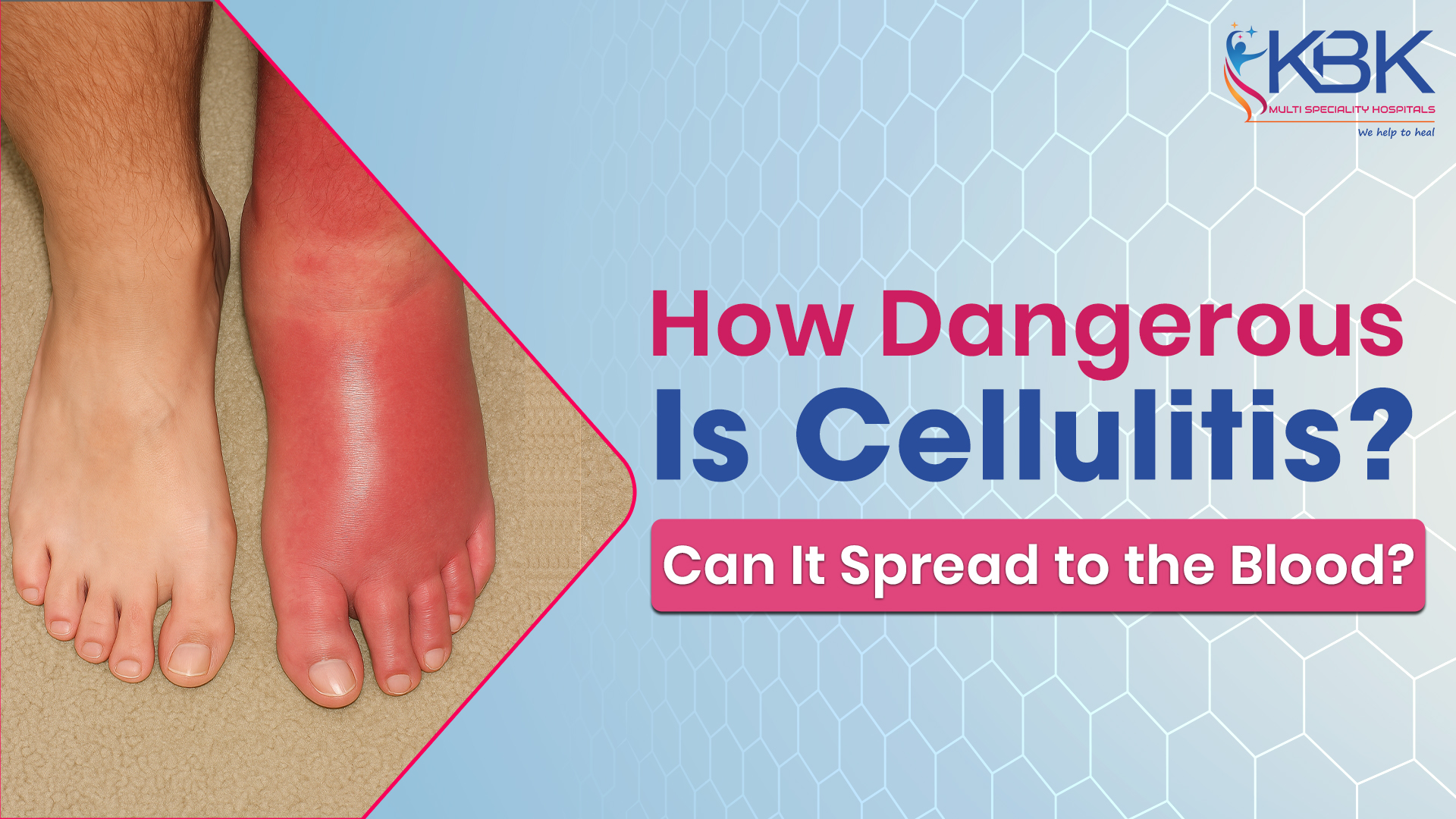
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can develop quickly if left untreated. Many people ask, how dangerous is cellulitis infection and whether it can spread to the blood. The answer depends on how early the condition is identified and treated.
Understanding Cellulitis Infection
Cellulitis begins when bacteria such as Streptococcus or Staphylococcus enter the skin through a cut, scrape, or wound. It commonly affects the legs, but it can occur on any part of the body. Typical symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, and warmth in the affected area.
How Dangerous Is Cellulitis Infection?
Mild cellulitis can often be managed with timely cellulitis treatment, but if ignored, it can progress into severe health problems:
- Rapid spreading – The infection can quickly spread to nearby tissues, making it harder to control.
- Abscess formation – Painful pus-filled pockets may develop, sometimes requiring surgical drainage.
- Permanent tissue damage – Severe or untreated cases may damage skin, fat, and muscle layers, leading to scarring.
- Infection of deeper structures – In rare cases, cellulitis can spread to joints, bones, or the lymphatic system.
- Recurrent episodes – Once the lymphatic system is damaged, cellulitis may keep returning.
Can Cellulitis Spread to the Blood?
Yes. If untreated, cellulitis can spread to the bloodstream, leading to sepsis, a life-threatening medical emergency. Some warning signs include:
- High fever and chills – Indicating the body’s immune system is overwhelmed.
- Fast heartbeat and rapid breathing – Early symptoms of sepsis and systemic infection.
- Confusion or dizziness – Showing that the infection is affecting body organs.
- Red streaks on the skin – A clear sign that bacteria are spreading through lymphatic vessels.
- Drop in blood pressure – A late-stage symptom of septic shock, requiring immediate hospitalization.
Without urgent cellulitis disease treatment, sepsis can cause organ failure or even death.
Importance of Timely Treatment
The good news is that cellulitis is treatable. Mild infections are usually managed with oral antibiotics, while severe cases may need intravenous medications in a hospital setting. Completing the full course of cellulitis treatment is vital to prevent recurrence or complications.
Final Thoughts
So, how dangerous is cellulitis infection? The danger lies in delay. Mild cellulitis is manageable, but untreated infections can spread to the blood and become life-threatening. Seeking prompt cellulitis disease treatment not only prevents severe complications but also ensures a faster and safer recovery.