Introduction:
Sepsis is a medical complication, that sometimes leads to multiple organ failure or even death. With the increasing cases of sepsis, more people need to know what it is and how to treat it. Properly understanding sepsis treatment and prevention with sepsis symptoms can significantly reduce your risk of contracting sepsis. You need to follow some simple terms to reduce the chances of sepsis infection. Here we will discuss about Sepsis treatment and prevention, causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods.
What is Sepsis?
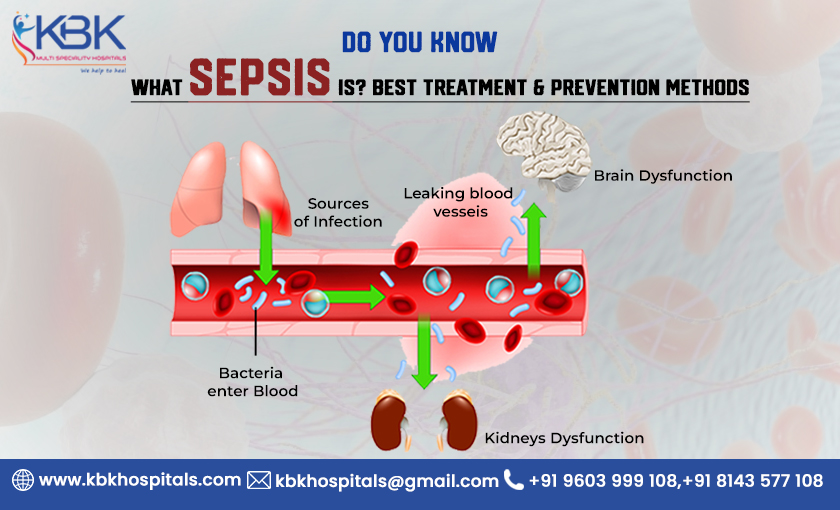
Sepsis is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when the body’s response to infection causes damage to its tissues. That infection may be through bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites. When the body’s response to these infections causes widespread inflammation throughout the body’s tissues leading to potentially fatal damage. Sepsis may range from mild to severe if you are left untreated for a long time.
Causes of Sepsis:
Sepsis is typically caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection that enters the bloodstream. Despite this, sepsis can be caused by many factors. Such as:
- Infections start in one part of the body and spread to the bloodstream.
- Infections enter the body through a wound or surgical incision.
- Infections occur as a medical procedure or treatment complication, such as a catheter or IV line.
- Non-infectious factors, such as burns, trauma, or pancreatitis, can cause sepsis.
Except for these, sepsis infects different parts of the body. Such as:
- It can affect your lungs, which is known as pneumonia.
- It can affect your urinary tract system, and you feel like you have a catheter there.
- It can affect your abdominal cavity and your liver.
Different stages of sepsis:
Sepsis is a severe emergency condition that requires immediate medical attention. It begins with an infection, which then triggers an overreaction of the body’s immune system, leading to a sepsis infection.
Septic shock, severe sepsis, and sepsis are the three main stages of sepsis.
In sepsis, such as impaired cognition or kidney dysfunction, mild organ failure may occur.
There can be severe organ damage due to sepsis infection in severe sepsis.
Septic shock is life-threatening and involves extreme blood pressure lowering due to sepsis.
Symptoms of Sepsis:
The symptoms of sepsis can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health. It shows many types of symptoms, as it affects different body parts. If symptoms of blood infection showing through your condition, your skin may develop a sepsis rash with red color. Severe breathlessness with high and low temperatures are some main sepsis symptoms in adults.

Some common symptoms of sepsis include:
- Fever or low body temperature
- Rapid heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion or disorientation
- Fatigue or weakness
- Chills or shivering
- Sweating
- Decreased urine output
If sepsis is not treated promptly, it can progress to severe sepsis or septic shock, which can cause additional symptoms such as:
- Difficulty breathing
- Blue lips or skin
- Severe abdominal pain
- Low blood pressure
- Loss of consciousness
Who is impacted by sepsis?
- Sepsis is a severe medical condition that affects people of all ages, from infants to the elderly.
- People with weakened immune systems due to chronic conditions or medications are at the highest risk for sepsis.
- People having severe injuries also have a chance of sepsis infection.
- People suffering from health issues or in hospital for a long time also can get sepsis infection.
Unfortunately, sepsis is only well-known by many people once they have had personal experience with it. So it is essential to recognize the signs of sepsis and symptoms early so Sepsis treatment and prevention can begin promptly to stop the infection from turning life-threatening.
Treatment of Sepsis:

Treatment is essential in Sepsis treatment and prevention, as it can progress rapidly and become life-threatening. With proper treatment and care can give you a chances of life expectancy after sepsis. The sepsis diagnosis process typically involves addressing the underlying infection to provide supportive care. That will help the body to fight the infection and maintain vital organ function.
Some common Sepsis treatment and prevention include:
Antibiotics: If the infection reason is bacteria, antibiotics are typically the first line of treatment. The choice of antibiotic will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection and its sensitivity to different antibiotics.
IV fluids: In some cases, sepsis can cause dehydration and low blood pressure. So IV fluids can help the body maintain blood pressure and hydration levels.
Oxygen therapy: If the person is having difficulty breathing, oxygen therapy may be necessary to ensure adequate oxygen levels.
Vasopressors: If the person’s blood pressure is severely low and not responding to IV fluids, vasopressor medications can help to increase blood pressure and improve organ perfusion.
Corticosteroids: In some cases, corticosteroids may be necessary to help reduce inflammation and improve organ function.
Other treatments: In some severe cases for Sepsis treatment and prevention, additional treatments may be necessary, such as mechanical ventilation or dialysis.
Surgery: If the infected tissue or organ is completely damaged, surgery is needed to remove that part.
Prevention of Sepsis:

While it is not always possible to prevent sepsis, there are some steps to follow to reduce the risk of developing the condition. Some prevention methods include:
Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly, especially before and after preparing food, after using the bathroom, and after coming into contact with someone sick.
Keep wounds clean and covered: If you have a wound, keep it clean and covered to prevent infection.
Get vaccinated: Vaccines can help prevent some infections that can lead to sepsis, such as influenza and pneumococcal disease.
Treat infections promptly: If you develop an infection, seek medical treatment to prevent it from progressing to sepsis.
Manage chronic conditions: If you have a chronic condition such as diabetes or heart disease, you may weaken your immune system. Just manage your health conditions carefully and consult a doctor to reduce the risk of developing sepsis. Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Sleep well, maintain a healthy diet, and exercise daily. This will help strengthen your immune system and reduce the risk of developing infections.
Conclusion:
Sepsis can be severe, but you can protect yourself by practicing good hygiene, staying up-to-date with vaccinations, managing chronic conditions, and recognizing the signs of sepsis and symptoms of sepsis. KBK Multispeciality hospital teaches proper hygiene practices as part of its awareness program. This can be instrumental in improving health conditions to avoid sepsis cases. A comprehensive range of preventive care facilities is available at KBK Multispecialty hospital. Take a look at our facilities once and see what we have to offer.
FAQs –
1. What does sepsis do to the body?
When an infection you already have causes a chain reaction throughout your body, you develop sepsis. Sepsis-causing infections frequently begin in the skin, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, or lungs. Without prompt treatment, sepsis can quickly cause organ failure, tissue damage, and death. If you notice the earlier symptoms of sepsis and start treatment, there are fewer chances of organ damage or long-term disability. It’s essential that anyone exhibiting sepsis symptoms contacts their primary care provider or nearest hospital immediately so they can receive necessary healthcare on time.
2. Are sepsis and septic the same thing?
The term “septic” is considerably different from “sepsis” to an infectious disease doctor. A septic denotes the presence of bacteria or other infectious elements, while sepsis is a severe immunological reaction to infection. The word “septic” refers to a patient with sepsis-like symptoms whose bacterial diagnosis may not be immediately apparent.
3. Can sepsis be cured?
Sepsis can be curable if you start its treatment quickly. Usually, there is a full recovery and no long-term issues. Early recognition and proper treatment can cure sepsis. The treatment plan includes IV fluids, oxygen therapy, medications to support blood pressure, etc. If any organ system is affected by sepsis, some special therapies are there to treat this sepsis.
4. Why is sepsis dangerous?
Sepsis can be life-threatening, especially if it is not treated quickly and correctly. At its worst, sepsis can lead to septic shock, multiple organ failure, or even death. It is essential that sepsis is caught early and treated on time to reduce the risk of severe health complications or death. Treatment for sepsis usually involves antibiotics to fight the infection, fluids to replenish blood volume, close monitoring of vital signs, oxygen therapy if needed, and other medications that may be necessary depending on the individual patient’s situation. By taking these steps immediately upon sepsis diagnosis, sepsis patients can have a better chance at successful treatment and complete recovery.
5. How is sepsis treated?
Sepsis treatment is an urgent and essential matter, depending on the severity of sepsis symptoms. As per the severity of sepsis, hospitals, and medical professionals use different approaches to sepsis treatment. This approach may include administering fluids to restore lost blood volume, antibiotics, and medications to help maintain adequate organ functioning. Sepsis treatments aim to prevent and manage long-term sepsis consequences, such as tissue damage and organ failure. The goal of sepsis treatment is to quickly address underlying causes while addressing potential complications before they become too severe.