Introduction –
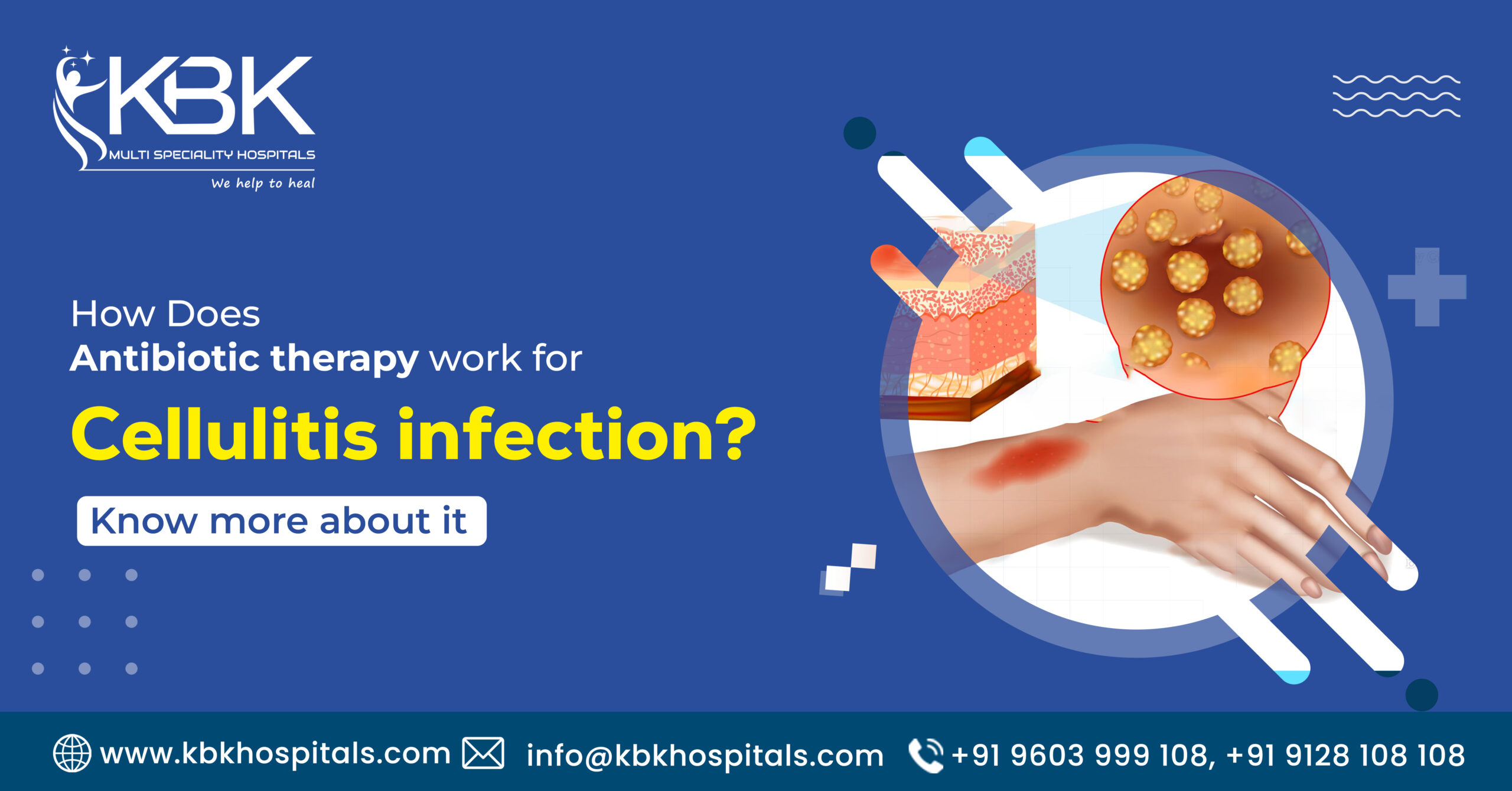
Cellulitis is a severe skin infection whose main cause is bacteria. When the skin is affected by Cellulitis, it swells, and the skin color changes. It is very painful that the patient even can’t walk properly. When considering the course of action for cellulitis treatment, there has been an increase in people opting for cellulitis antibiotics therapy. Antibiotic therapy is vital to treating any type of skin infection.
It should always be considered if proper healing is required. However, many people are unfamiliar with how exactly cellulitis antibiotics therapy works. Here you will get all the information on cellulitis treatment through antibiotic therapy when treating cellulitis infections. So read it completely to learn more about what makes choosing antibiotics such an important decision and whether or not they are effective in helping treat this particular skin condition.
What are the Cellulitis Symptoms?
Cellulitis is a Common skin condition that can cause red, swollen, and tender skin. It often starts as a small spot or patch before quickly spreading across the body with accompanying fever, chills, and blisters. In some cases, it might even lead to dimpling in the affected region. So if you notice any of these signs, seek medical advice earlier to stop more infection.
The Role of Antibiotic Therapy for Cellulitis Treatment:
Antibiotic therapy is the mainstay of cellulitis treatment. The goal of antibiotic therapy is to kill the bacteria causing the infection and prevent the spread of the infection. Antibiotics work by killing bacteria or preventing them from multiplying. When antibiotics are taken for Cellulitis, they are usually prescribed for at least ten days or until the infection has cleared up. The antibiotic prescribed will depend on the severity of the infection, the type of bacteria causing the infection, and the patient’s medical history.
Types of Antibiotics for Cellulitis Treatment:
Cellulitis has a common cause, such as staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria. Mostly these are dangerous for legs. So cellulitis leg treatment is required early to stop infection. Fortunately, these infections can be treated with antibiotics that specifically target the underlying causes of this skin condition. Oral medications have proven effective relief for most people with cellulitis symptoms.
Regarding antibiotics, several types of antibiotics are used to treat Cellulitis. The most common antibiotics used are penicillin, cephalosporins, and macrolides.
Penicillin –
Penicillin is the most common antibiotic for treating bacterial Cellulitis because it is effective against most bacteria that cause skin infections. It works by inhibiting the bacterial cell wall synthesis, ultimately leading to bacterial death.
Cephalosporins –
Cephalosporins are another class of antibiotics that can effectively treat skin cellulitis. They work by interfering with the ability of bacteria to form their cell walls, which are necessary for their survival. Cephalosporins bind to specific enzymes involved in the cell wall synthesis process. This prevents the bacteria from constructing a strong and stable cell wall. As a result, the bacteria become weakened and leading to their death. Cephalosporins are effective against many bacteria, including those that cause Cellulitis. Mostly these are often used as a first-line treatment for this condition.
Macrolides –
Macrolides are also used as antibiotics that are often used to treat Cellulitis. They work by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, which prevents bacteria from multiplying and ultimately leads to bacterial death. Specifically, macrolides bind to the bacterial ribosome, preventing adding new amino acids to the growing protein chain. This leads to the formation of incomplete. It disrupts the normal functioning of the bacterial cell and eventually causes its death. By targeting these essential bacterial processes, macrolides effectively kill bacteria and stop the progression of Cellulitis.
The Success of Antibiotic Therapy for Cellulitis Treatment:
The success of antibiotic therapy for Cellulitis depends on several factors. The severity of the infection, the type of bacteria causing the infection, and the patient’s medical history will all play a role in determining the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. Antibiotic therapy may sometimes not work, and more aggressive treatment may be necessary, such as surgery or intravenous antibiotics.
When to visit your doctor?
Ensuring that you get the best possible care is essential when it comes to a diagnosis of Cellulitis. Because this condition can spread quickly throughout your body. If you notice any signs, such as an expanding or tender rash with or without fever, seek medical attention immediately for emergency care if needed. Otherwise, make an appointment to see your doctor within 24 hours. Treating and identifying these symptoms early on could save much suffering in the long run.
How to take Antibiotics?
It is essential to take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Failure to complete the entire course of antibiotics can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which can make future infections more difficult to treat. In addition, antibiotics can have side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and allergic reactions. You should contact your doctor immediately if you experience any side effects while taking antibiotics.
Conclusion –
In sum, understanding how your body naturally responds to cellulitis infection can help prevent it from occurring in the first place. Antibiotic therapy success depends on the infection’s severity, the type of bacteria causing the infection, and the patient’s medical history. Additionally, recognizing the signs and symptoms of the infection early on can ensure that any antibiotic treatments administered reach their most influential state and prevent further spread.
If you understand how it works for treating Cellulitis infection, you’ll be more likely to remain pain-free during the entire process. If you want antibiotic therapy for Cellulitis infection, visit KBK Multispeciality Hospital. It is one of the top-rated hospitals providing world-class medical treatment. Our service is based on empathy, trust, and extraordinary clinical results with an uncompromising commitment toward our patients.
FAQs
1. What is the first choice of Antibiotic for cellulitis?
According to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), it’s usually penicillin or a cephalosporin antibiotic. However, the specific type and antibiotic dosage can vary depending on the severity of the infection and individual patient factors.
2. What Antibiotics are used for Cellulitis in the leg?
The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for cellulitis include penicillin, amoxicillin, and Cephalosporins. However, the type of antibiotic prescribed may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria causing it. It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect cellulitis leg, as treating it earlier can prevent the infection from becoming more serious.
3. What is the Strongest Antibiotic for Cellulitis?
The strongest antibiotic for cellulitis will depend upon the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria that is causing it. The most commonly used antibiotics include penicillin, erythromycin, cephalosporin, and clindamycin. But you need to consult with a healthcare professional before self-treating with antibiotics to ensure proper dosage and effectiveness.
4. What helps Cellulitis heal faster?
First, taking any antibiotics, your doctor prescribes as directed is important. Additionally, keeping the affected area elevated and applying warm compresses can help reduce swelling and inflammation. Avoiding tight clothing or bedding that rubs against the area and keeping the area clean and dry can also aid healing. With proper medical treatment and self-care, you can return to feeling like your healthy self in no time.
5. How long should you take Antibiotics for Cellulitis?
Stopping the medication too soon can increase the likelihood of the infection returning. But continuing to take antibiotics for too long can lead to antibiotic resistance. Your healthcare provider can guide the most appropriate duration of antibiotic treatment based on your case and medical history. But one thing is for certain. Completing the full course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better after a few days, is crucial in fighting the infection and preventing long-term complications.