Understanding the difference between necrosis and gangrene is important because both conditions involve damaged body tissues, but they are not the same. Many people confuse them, but learning how they differ helps you recognize symptoms early and get the right care at the right time.
What Is Necrosis?
Necrosis is the death of body tissue caused by factors like poor blood flow, infection, toxins, or injury. When cells stop receiving oxygen and nutrients, they break down and the affected area cannot heal on its own. This process may occur anywhere in the body and often starts silently, especially when related to internal infections or blocked blood vessels. Without timely care, necrosis can worsen and may lead to more severe complications.
What Is Gangrene?
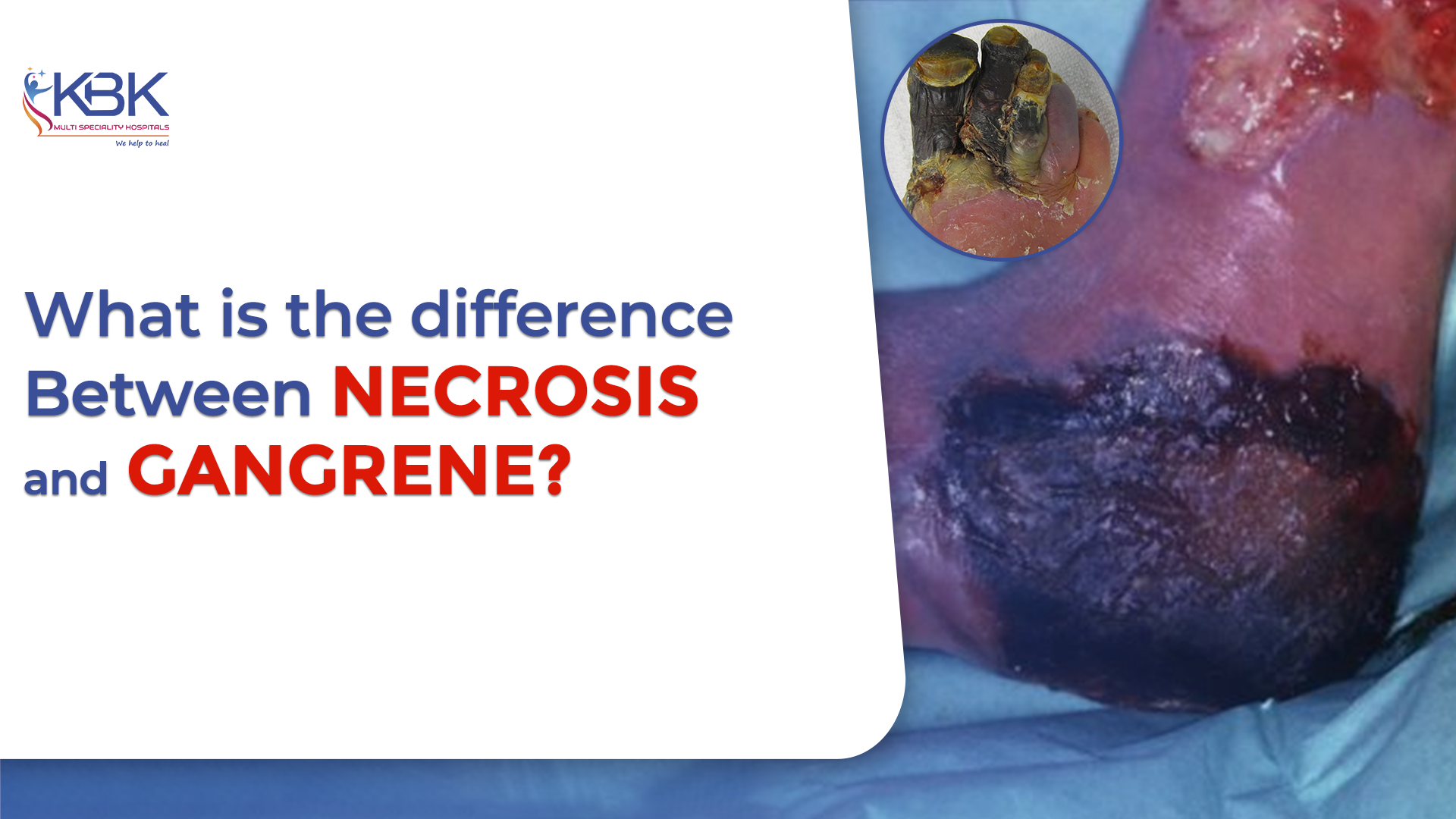
Gangrene is a more advanced and serious condition that develops when necrotic (dead) tissue becomes infected or when blood supply to an area becomes extremely low. It commonly affects areas like the toes, fingers, feet, and legs. People with diabetes, poor circulation, severe infections, or injuries have a higher chance of developing gangrene.
Unlike necrosis, gangrene shows clear outward symptoms such as:
- Skin discoloration
- Bad smell
- Swelling
- Severe or continuous pain
Without proper gangrene treatment, the infection can spread quickly and damage healthy tissues.
Key Difference Between Necrosis and Gangrene
The main difference between necrosis and gangrene is that:
- Necrosis is simply tissue death
- Gangrene is tissue death combined with infection or extremely poor blood flow
Gangrene is more dangerous because the infection can move fast and cause life-threatening complications.
Why Early Detection Matters
Both conditions require quick medical attention, but gangrene needs immediate care. Early detection helps prevent the infection from spreading and reduces the risk of severe damage. For people with diabetes or poor circulation, routine checkups and proper wound care are essential to stop necrosis from developing into gangrene.
How Gangrene Is Treated
Modern gangrene treatment focuses on improving blood flow, controlling infection, cleaning the affected area, and promoting natural healing. Getting early treatment for gangrene can protect the affected part, stop complications, and support faster recovery.
Conclusion
In simple terms, necrosis is tissue death, while gangrene is tissue death with infection. Understanding the difference between necrosis and gangrene helps you act fast and get expert care. Early and proper gangrene treatment plays a major role in preventing further tissue damage and protecting your health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What causes necrosis?
Necrosis happens when a part of the body does not get enough oxygen or nutrients. This can occur due to poor blood flow, infections, toxins, injuries, or underlying health issues like diabetes or blocked arteries.
2. Is necrosis the same as gangrene?
No. Necrosis is tissue death, while gangrene is tissue death with infection or very poor blood flow. Gangrene is more serious and needs urgent medical care.
3. What symptoms should I look for in gangrene?
Gangrene usually shows clear signs such as:
- Dark or discoloured skin
- Bad smell
- Swelling
- Severe or constant pain
If you notice these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
4. Can necrosis turn into gangrene?
Yes. If necrotic (dead) tissue becomes infected or if blood flow becomes worse, it can develop into gangrene. This is why early treatment is very important.
5. Who is at higher risk of developing gangrene?
People with:
- Diabetes
- Poor blood circulation
- Severe infections
- Foot wounds or injuries have a higher chance of developing gangrene, especially in the legs, feet, toes, and fingers.
6. How is gangrene treated?
Gangrene treatment focuses on:
- Improving blood circulation
- Controlling infection
- Cleaning the damaged area
- Supporting natural healing
Early treatment helps prevent complications and protects healthy tissues.
7. Can necrosis heal by itself?
No. Once tissue dies, it cannot repair itself. Medical care is needed to stop necrosis from spreading and to prevent infection.
8. How can I prevent necrosis and gangrene?
You can reduce the risk by:
- Managing diabetes or vascular conditions
- Checking your feet regularly
- Treating wounds early
- Keeping good hygiene
- Improving circulation through healthy habits
9. When should I see a doctor?
Seek immediate medical help if you notice:
- Sudden skin colour changes
- Unusual smell
- Increasing pain
- Non-healing wounds
Early care can prevent complications and protect your overall health.